Great Dividing Range
| Great Dividing | |
| Eastern Highlands, Great Divide | |
| Range | |
 |
|
| Country | Australia |
|---|---|
| States | New South Wales, Queensland, Victoria (Australia) |
| Highest point | Mount Kosciuszko |
| - elevation | 2,228 m (7,310 ft) |
| - coordinates | |
| Length | 3,500 km (2,175 mi), North-South |
The Great Dividing Range, or the Eastern Highlands, is Australia's most substantial mountain range and the fourth longest in the world. The range stretches more than 3,500 km (2,175 mi) from Dauan Island off the northeastern tip of Queensland, running the entire length of the eastern coastline through New South Wales, then into Victoria and turning west, before finally fading into the central plain at the Grampians in western Victoria. The width of the range varies from about 160 km to over 300 km.[1]
The sharp rise between the coastal lowlands and the eastern uplands has affected Australia's climate, mainly due to orographic precipitation, and these areas of highest relief have revealed an impressive gorge country.[2]
Contents |
Terminology
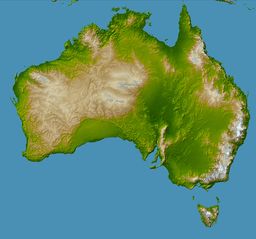
The Dividing Range does not consist of a single mountain range. It consists of a complex of mountain ranges, plateaus, upland areas and escarpments with an ancient and complex geological history. The physiographic division name for the landmass is called the East Australian Cordillera.
The crest of the range is defined by the watershed or boundary between the drainage basins of rivers which drain directly eastward into the Pacific Ocean, or southward into Bass Strait, and those rivers which drain into the Murray-Darling River system towards the west and north. In the north, the rivers on the west side of the range drain towards the Gulf of Carpentaria.
It should be noted that the higher and more rugged parts of the "range" do not necessarily form part of the crest of the range, but may be branches and offshoots from it. The term "Great Dividing Range" may refer specifically to the watershed crest of the range, or to the entire upland complex including all of the hills and mountains between the east coast of Australia and the central plains and lowlands. Notable ranges and other features which form part of the range complex have their own distinctive names.
History
The ranges were originally home to Australian Aboriginal tribes. Evidence remains in some places of their occupation by decorated caves, campsites and trails used to travel between the coastal and inland regions.
After European settlement in 1788, the ranges were an obstacle to exploration and settlement by the British settlers. Although not high, parts of the highlands were very rugged.
In 1813, a usable route was finally discovered directly westward from Sydney across the Blue Mountains to Bathurst by the party of Gregory Blaxland, which included William Lawson and William Charles Wentworth. (Towns in the Blue Mountains were later named after each of these men.) This was the start of the development of the agricultural districts of inland New South Wales. Easier routes to inland New South Wales were discovered towards Goulburn to the southwest, and westwards from Newcastle.
Subsequent explorations were made across and around the ranges by Allan Cunningham, John Oxley, Hamilton Hume, Ludwig Leichhardt and Thomas Mitchell. These explorers were mainly concerned with finding good agricultural land.
By the late 1830s the most fertile rangelands adjacent to the mountains ranges had been explored and some settled. These included the Gippsland and Riverina regions in the south, up to the Liverpool Plains and the Darling Downs in the north.
Various road and railway routes were subsequently established through many parts of the ranges, although many areas remain remote to this day. For example, in eastern Victoria there is only one major road crossing the highlands from north to south.

Notable components
Parts of the highlands consisting of relatively flat and, by Australian standards, well-watered land were developed for agricultural and pastoral uses. Such areas include the Atherton Tableland and Darling Downs in Queensland, and the Northern Tablelands, Southern Highlands and Southern Tablelands in New South Wales. Other parts of the highlands are too rugged for agriculture and have been used for forestry. Many parts of the highlands which were not developed are now included in National Parks.
All of mainland Australia's alpine areas, including its highest mountain, Mount Kosciuszko (2,228 metres AHD), are part of this range. The highest areas in southern New South Wales and eastern Victoria are known as the Australian Alps.
The central core of the Great Dividing Range is dotted with hundreds of peaks and is surrounded by many smaller mountain ranges or spurs, canyons, gorges, valleys and plains of regional significance. Some of the major plains include the High Plains of South-Eastern Australia, the Southern Highlands the Central highlands and Bogong High Plains of Victoria. Other tablelands considered part of the Great dividing range are the Atherton Tableland, Canberra wine region and the Southern Tablelands.
The Dandenong Ranges, Bunya Mountains, Blue Mountains, Liverpool Range, McPherson Ranges and the Moonbi Range are some of the smaller spurs and ranges that make up the greater dividing range. Other notable ranges and tablelands which form part of the Great Dividing Range include the Liverpool Range, Mount Royal Range and the Monaro District. Whilst some of the peaks of the highlands reach respectable heights of a little over 2,000 metres, the age of the range and its erosion mean that most of the mountains are not very steep, and virtually all peaks can be reached without mountaineering equipment.
In some areas, such as the Snowy Mountains, Victorian Alps, the Scenic Rim and the eastern escarpments of the New England region, the highlands form a significant barrier. The eastern escarpment is the site of many spectacular waterfalls which were formed by rivers plunging off the tablelands. In other areas the slopes are gentle and in places the range is barely perceptible.[1]
Well known passes on the range include Coxs Gap, Cunninghams Gap, Dead Horse Gap, Nowlands Gap, and Spicers Gap.

Notable towns located on the upland areas of the range include Atherton, Toowoomba, Armidale, Oberon, Goulburn, Canberra, Walcha and Omeo. Many other towns and cities are located in lowland areas and foothills adjacent to the highlands. There is a strong natural history and cultural attachment to the Dividing Range region in towns and on and many, sometimes remote landholdings.
Water catchments
The lower reaches are used for forestry, an activity that causes much friction with conservationists. The ranges is also the source of virtually all of eastern Australia's water supply, both through runoff caught in dams, and, throughout much of Queensland, through the Great Artesian Basin.
Valleys along the chain of mountains have yielded a water source for important reservoirs and water supply projects such as the Upper Nepean Scheme, Snowy Mountains Scheme and Warragamba Dam. The Bradfield Scheme has been mooted as a way to transport water from the tropics in coastal Queensland south to dryer regions.
The Great Dividing Range creates the drainage basins of the Australian south-east coast drainage division and the Australian north-east coast drainage division, whose water flows to the east coast and into the Pacific Ocean, Tasman Sea, and Bass Strait with the westerly Murray-Darling Basin which flow inland, away from the coast into the interior plains.
Some of the rivers which flow west of the ranges includes the Condamine River, Flinders River, Herbert River, Lachlan River, Macdonald River, Macintyre River and Namoi River. Rivers that flow north into the Murray-Darling Basin from Victoria include the Goulburn, Mitta Mitta, Kiewa, Ovens. King, Loddon and Campaspe rivers. Rivers that flow east into the Pacific Ocean include the Brisbane River, Burdekin River, Clarence River, Hastings River, Hawkesbury River, Hunter River, Macleay River, Mary River, Richmond River, Shoalhaven River and the Snowy River. Those that flow south to the ocean in Victoria include the Snowy, Cann, Tambo, Mitchell, Latrobe, Thomson, Yarra, Werribee, Hopkins and Glenelg rivers.
Features

Railways
The engineers of early rail passages across the Great Dividing Range needed to find low sections of the range to cross, as well as suitable, low gradient paths up the mountains on either side. Rail passages include:
- Ipswich-Toowoomba (1867)
- Newcastle-Tamworth (c1870) - summit at Ardglen Tunnel
- Sydney-Lithgow (1869), crossing the range via the Blue Mountains
- Sydney-Goulburn (1869), though the divide is actually a few kilometres further west toward Cullerin
- Melbourne-Seymour, crossing the range near Heathcote Junction (1872)
- Melbourne-Bendigo, crossing the range near Woodend (1862)
- Melbourne-Ararat (1875) via Ballarat
Road Transport
Many of Australia's highways such as the Alpine Way, Great Alpine Road, Hume Highway, Great Western Highway, Capricorn Highway, Cunningham Highway, New England Highway, Oxley Highway, Warrego Highway, Waterfall Way, Thunderbolts Way the Calder Highway, the Western Highwayand the Murray Valley Highway traverse parts of the range.
Protected areas
Much of the range lies within a succession of national parks and other reserves, most of the national parks are listed below, there are almost double the amount of state forests;[3][4]
|
|
|


References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Shaw, John H., “Collins Australian Encyclopedia”, William Collins Pty Ltd., Sydney, 1984, ISBN 0 00 217315-8
- ↑ Löffler, Ernst; A.J. Rose, Anneliese Löffler & Denis Warner (1983). Australia:Portrait of a Continent. Richmond, Victoria: Hutchinson Group. ISBN 0091304601.
- ↑ Melways, Edition 35 2008, Touring Maps
- ↑ Brisway, Edition 1, 2005